Rear crash prevention
IIHS rates vehicles for rear crash prevention, a group of technologies that help drivers avoid colliding with other vehicles or fixed objects when traveling in reverse. The technologies include parking sensors, rear automatic braking and rear cross-traffic alert.
The ratings are based on the presence of parking sensors and rear cross-traffic alert and, for autobrake, the system’s performance in a series of track tests at 4 mph. Vehicles with rear crash prevention technologies can be rated basic, advanced or superior.
Rated vehicles
Front crash prevention - superior
Superior
- 2023-24 Ford Escape
Optional - 2023-24 Honda CR-V
Optional - 2023-24 Mitsubishi Outlander
Standard - 2023-24 Subaru Forester
Optional - 2017-19 Cadillac XT5
Optional - 2019 Subaru Ascent
Optional - 2018-19 Subaru Crosstrek
Optional - 2018-19 Subaru Impreza sedan & wagon
Optional - 2018-19 Subaru Legacy
Optional - 2017-19 Subaru Outback
Optional - 2018-19 Subaru WRX
Optional
Front crash prevention - advanced
Advanced
- 2023-24 Mazda CX-5
Optional - 2023-24 Toyota RAV4
Optional - 2023-24 Volkswagen Taos
Optional - 2017-19 BMW 5 series sedan
Optional - 2017-19 Infiniti QX60
Optional - 2017-19 Jeep Cherokee
Optional - 2019 RAM 1500
Optional - 2017-18 Toyota Prius
Optional
Front crash prevention - basic
Basic
- 2023-24 Hyundai Tucson
Standard rear automatic braking; other functions optional
Test scenarios
The rear autobrake tests are based on a protocol developed by RCAR, an international consortium of insurance-funded research organizations working to reduce the injuries and property damage associated with automobile crashes.
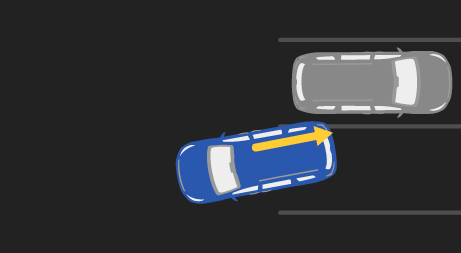
Reversing car-to-car, 16" overlap:
This scenario simulates backing out of a parking space toward a stationary vehicle (shown in gray). Test runs include reversing straight back and from the left and right toward the target. If autobrake fails to prevent a collision, the test vehicle will strike the corresponding portion of the target vehicle bumper with an overlap of 16 inches.
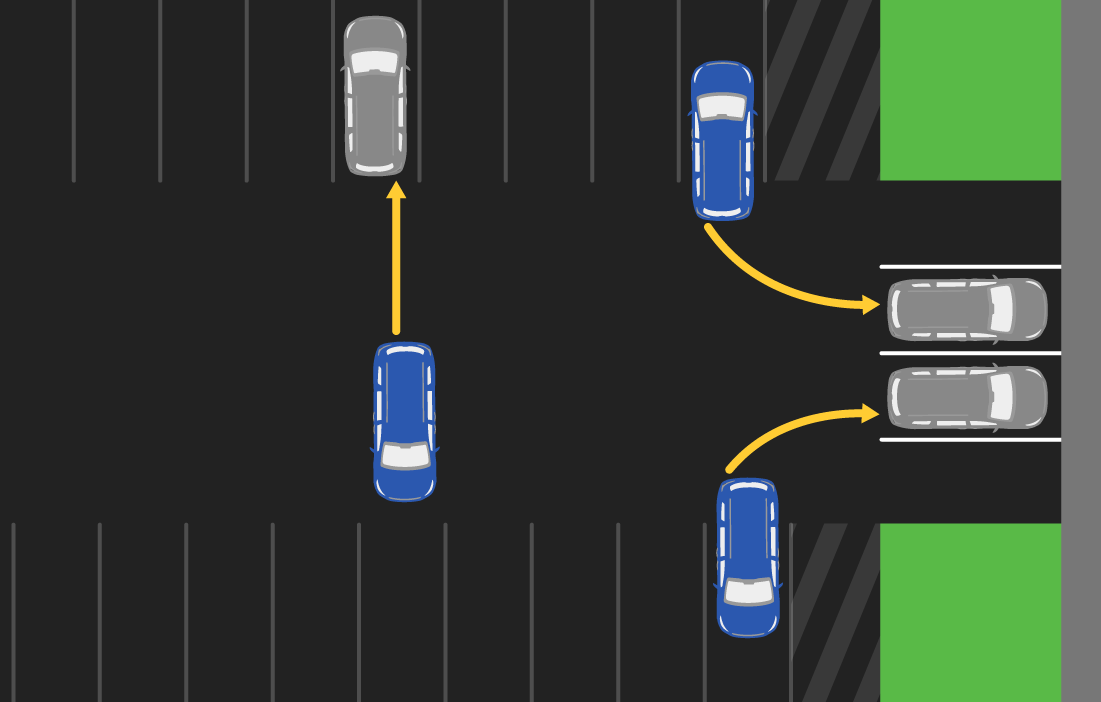
Reversing car-to-car, 45° angle:
This scenario involves reversing out of a parking space toward a stationary vehicle (shown in gray). Test runs include reversing straight back and from the left and right toward the target. If autobrake fails to intervene, the corner of the test vehicle's bumper will strike the center of the target vehicle bumper.
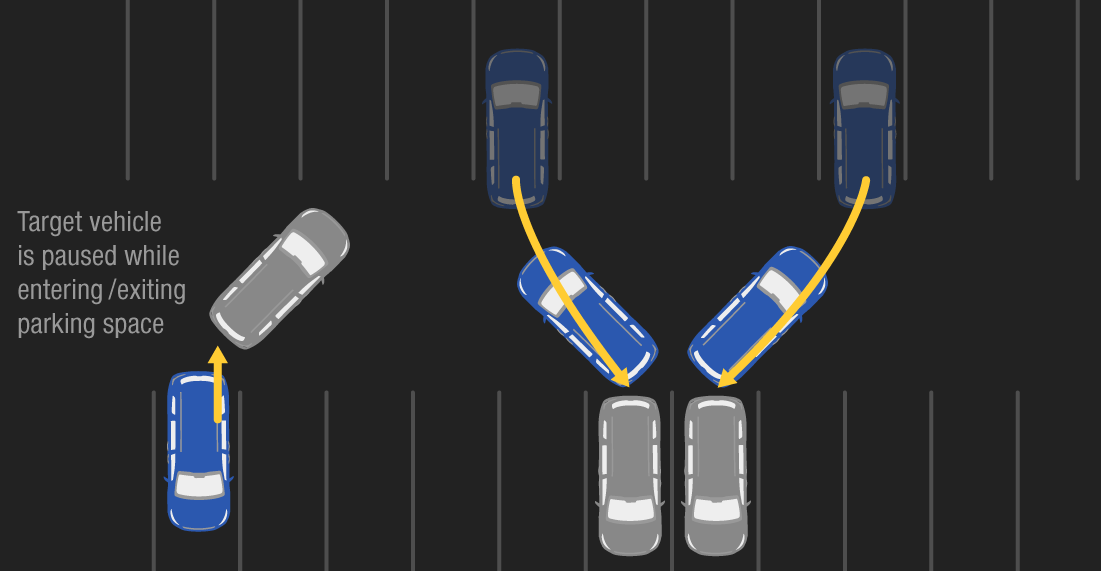
Reversing car-to-car, 10° angle:
This scenario simulates backing toward the side of an adjacent stationary vehicle (shown in gray). The test involves reversing straight back toward the target vehicle parked at a 10° angle to the test vehicle.

Reversing toward fixed pole:
This scenario simulates backing into a pole or garage pillar. The test car reverses straight toward a bollard that is aligned midway between the center line and bumper corner.
How points are assigned
In the ratings, autobrake carries the most weight because research shows it provides the biggest crash reductions. For autobrake, systems are assigned points from the track tests based on the number of runs that either avoid or barely hit the target, reducing speeds to less than 1 mph.
| Point values for each autobrake test or non-autobrake feature | |
|---|---|
| Test vehicle traveling straight: 16-inch overlap, 45-degree angle, 10-degree angle | 2 points |
| Test vehicle traveling left: 16-inch overlap, 45-degree angle, 10-degree angle | 1 point |
| Test vehicle traveling right: 16-inch overlap, 45-degree angle, 10-degree angle | 1 point |
| Test vehicle into fixed object | ¾ point |
| Rear cross-traffic alert present | ¾ point |
| Rear parking sensors present | ½ point |
-
Front crash prevention - basic
Basic
0.5 to 1.4 points -
Front crash prevention - advanced
Advanced
1.5 to 4.4 points -
Front crash prevention - superior
Superior
4.5 to 6 points
Test protocol
Rear crash prevention test protocol Version I, July 2024